9. Measuring specific compounds: the example of dioxins
The pollutants that can be emitted into the air are very numerous and cannot be exhaustively described here. In each case, we can draw on the various techniques described so far. The case of dioxins will be dealt with here by way of example only.
9.1 Properties of dioxins
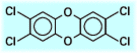
The term dioxin refers to a family of hydrocarbons made up of 2 chlorinated aromatic rings (1 to 8 atoms in all) joined by one or two oxygen atoms:
.
Exclusive to subscribers. 97% yet to be discovered!
You do not have access to this resource.
Click here to request your free trial access!
Already subscribed? Log in!

The Ultimate Scientific and Technical Reference
This article is included in
Environment manager
This offer includes:
Knowledge Base
Updated and enriched with articles validated by our scientific committees
Services
A set of exclusive tools to complement the resources
Practical Path
Operational and didactic, to guarantee the acquisition of transversal skills
Doc & Quiz
Interactive articles with quizzes, for constructive reading
Measuring specific compounds: the example of dioxins
References
Exclusive to subscribers. 97% yet to be discovered!
You do not have access to this resource.
Click here to request your free trial access!
Already subscribed? Log in!

The Ultimate Scientific and Technical Reference