2. Thermodynamic principles of phase equilibrium
2.1 Thermodynamic definition of phase equilibrium
In thermodynamics, a closed system is defined as a certain quantity of matter with a constant number of moles of each constituent pure substance. The definition of chemical constituents is tricky for some systems, where chemical reactions can modify the list of pure bodies actually present in the system. But in the case of alloys, the definition of constituents is unambiguous: each chemical element in the system represents a constituent. Indeed, in many metallic phases, the structural entity is the atom, even if in some cases there are more complex entities with strong internal bonds.
The closed system is bounded by a system contour, the permeability of which must be defined with respect to exchanges with the outside....
Exclusive to subscribers. 97% yet to be discovered!
You do not have access to this resource.
Click here to request your free trial access!
Already subscribed? Log in!

The Ultimate Scientific and Technical Reference
This article is included in
Studies and properties of metals
This offer includes:
Knowledge Base
Updated and enriched with articles validated by our scientific committees
Services
A set of exclusive tools to complement the resources
Practical Path
Operational and didactic, to guarantee the acquisition of transversal skills
Doc & Quiz
Interactive articles with quizzes, for constructive reading
Thermodynamic principles of phase equilibrium
Diagram classification
In this folder, the diagrams are arranged in alphabetical order of the symbol of the element concerned, which comes first in alphabetical order among the elements making up the alloy; then, for a given element, in alphabetical order of the symbol of the second element.
Example
we find Fe-C to C-Fe.
...
Binary alloys containing Ag

Binary alloys containing Al
Binary alloys containing As
As-Cu (arsenic-copper – figure )
This diagram has recently been completely revised. The relationships between phases and their compositions are now well known; there are apparently no other intermediate phases richer in arsenic than those shown in the diagram.
-
Phase structures
(Cu) : c. f. c....
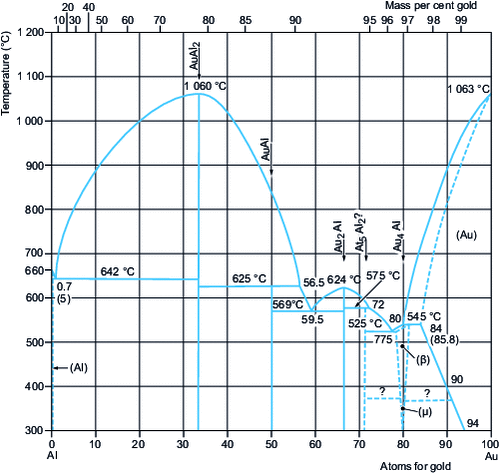
Au-containing binary alloys

Binary alloys containing either B, Be or Bi

Binary alloys containing C

Binary alloys containing either Ca, Cd or Ce

Binary alloys containing Co

Binary alloys containing Cr

Binary alloys containing Cu

Binary alloys containing Fe

Binary alloys containing Li, Mg or Mn

Binary alloys containing either Mo, or N, or Nb, or Ni, or O

Binary alloys containing either Pb, Sb, Sn or Ti

Exclusive to subscribers. 97% yet to be discovered!
You do not have access to this resource.
Click here to request your free trial access!
Already subscribed? Log in!

The Ultimate Scientific and Technical Reference